What is microstructure?
The microstructure is described as an arrangement of grains in the material's physical structure that is observed with the help of an optical instrument called a microscope.
The microstructure of crystalline materials depends on their type, dimension, topological arrangement of phase, and crystal lattice defects.
The diagrammatical representation of the microstructure of substance is shown as:
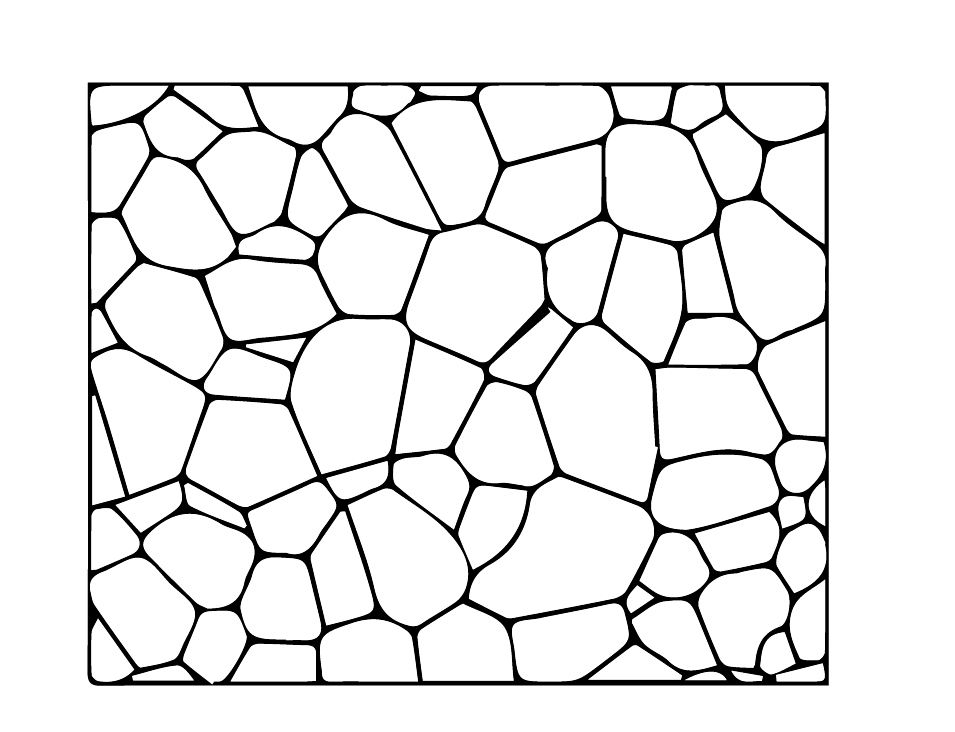
Element of microstructure
Following are the various elements of the microstructure of materials:
- Point defect
- Point defect clusters
- Dislocations
- Stacking faults
- Grain boundaries
- Interface
Defects in metals
Metal defects are the effect produced in metals to reduce their functional characteristics and durability. The defects in metal are generated due to the following reasons:
- Defects in metal due to the crystal structure
- Defects in metal due to casting technique
- Defects in metal due to fabrication technique
- Defects in metal due to metal forming technique
Defects in metal due to crystal structure
Following are the metal defects due to crystal structure is as follows:
- Point defect
- Line defect
- Surface defect
- Volume defect
Point defect
The point defect is a dimensional less defect that shows a point irregularity in a crystalline structure of the metal. Following are the various types of point defects:
- Vacancy defect
- Interstitial defect
- Schottky defect
- Frenkel defect
Line defect
The line defect is a unit dimensional defect generated in the crystal of metal due to the linear disarrangement of atoms. Following are the various types of line defects:
- Edge dislocation
- Screw dislocation
- Mixed dislocation
Surface defect
The surface defect is also known as area defect. It is a two-dimensional defect developed in the crystal structure of metal due to the stacking of the atomic plane with the crystal boundary. Following are the types of surface defects:
- External Surface Imperfection
- Internal Surface Imperfection
Volume defect
The volume defect in the metal surface mainly occurs due to atomic dissimilarities, void or cavity, impurity inclusion, and many more. It is a three-dimensional defect.
Defects in metal due to casting technique
Following are the common metal defects that occur in metals during their casting:
- Drop
- Buckle
- Scab
- Gas inclusion
- Discontinuities
- Inclusion
Drop
Drop-in metals occur in the form of irregular projection on the top of a casting caused due to dropping of sand from mold.
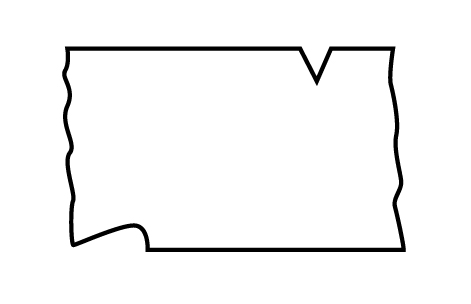
Buckle
The buckle is a defect observed over the metal surface as v-shaded depression on flat casting due to expansion of sand at the mold face before liquid metal solidifies. The diagrammatical representation of buckle is shown as:
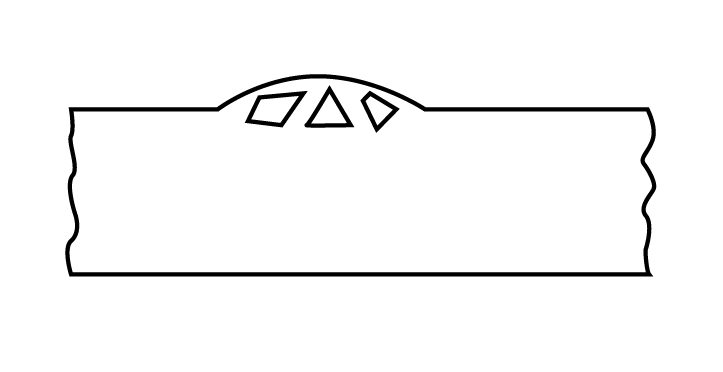
Scab
A scab is a protruding surface of casting at the roof. The diagrammatical representation of scab is shown as:
Gas inclusion
Gas inclusion occurs in metals due to the inclusion of air and other gases. It overcomes by using a proper venting arrangement to the casting mold.
Discontinuities
In discontinuities defect, the metal produced has no uniformity or has gaps in the material. It mainly occurs due to improper feeding, shrinkage of material, incorrect manufacturing arrangement, poor raw material, and many others.
Inclusion
The inclusion is a defect generated in metals due to some foreign substance. The inclusion of foreign substances changes the properties of base metal. Sometimes, inclusions are made intentionally to improve metal properties.
Defects in metal due to fabrication technique
Following are the defects that occur in metal due to fabrication is as follows:
- Porosity
- Slag inclusion
- Cracks
- Lamellar tears
- Weld spatter
Porosity
Porosity is developed due to the entrapment of gas bubbles during the cooling of the wed pool. It occurs only in the weld material. Porosity in metal is generally in the shape of a sphere or elongated holes.
Slag Inclusion
Slag inclusion is developed in the metal caused by compounds like oxides, flux, electron coating, and others trapped in metal during welding. It overcomes by cleaning the weld bead or providing shielding gas or additional chemical substance.
Cracks
Crack is the major defect in fabrication; it leads to premature failure of metallic components, particularly in the case of dynamic loading. Cracks during fabrication are mainly occurring due to thermal stresses and variations of composition in the weld zone.
Lamellar tears
Lamellar tears will appear over the metal surface due to shrinkage of the restrained components during cooling of the weld zone. It overcomes by providing free shrinkage of the members.
Weld spatter
Weld spatter are the small elements observed over the metal surface due to splashing of liquid metal on the base metal. It occurs mainly due to high welding power, low welding speed, arc blow, and many others.
Defects in metal due to metal forming technique
Following are the common types of metal forming defects:
- Rolling defect
- Extrusion defect
- Drawing defect
Rolling defect
Rolling defects occur over the metal surface during the rolling operation over the metal. Following are the various types of rolling defects:
- Wavy edges
- Spread
- Crocodile crack
- Alligatoring
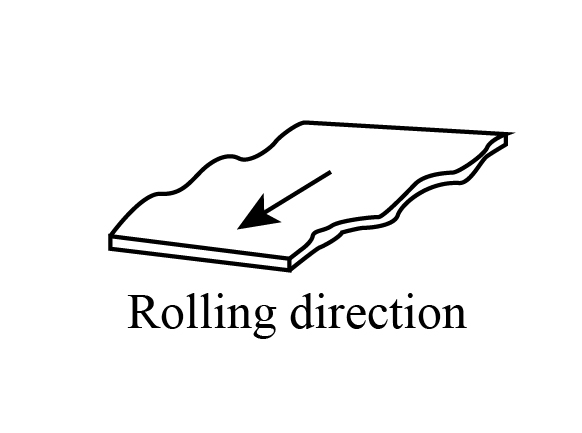
Wavy edges
Wavy edges are the result of roll bending. In this defect, the metal strip is thinner along its edge than the center, and waves are produced in the metallic strip.
The diagrammatical representation of wavy edges on the metal surface is shown as:
Spread
In the rolling process, the proper width and thickness ratio is achieved. But in spread defect, the width of metal increases largely when compared to its thickness which induces small holes in the middle of metal sheets. The diagrammatical representation of spread is shown as:
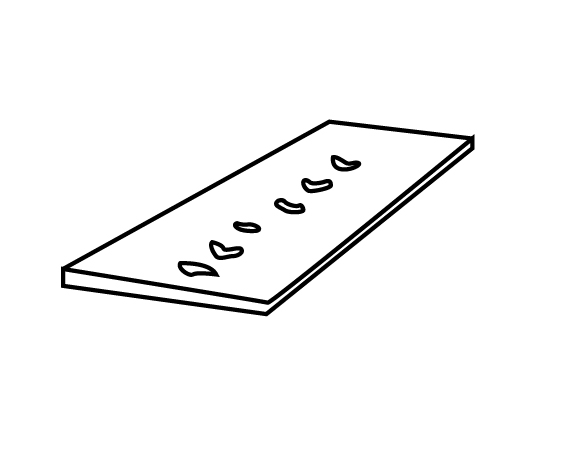
Crocodile crack
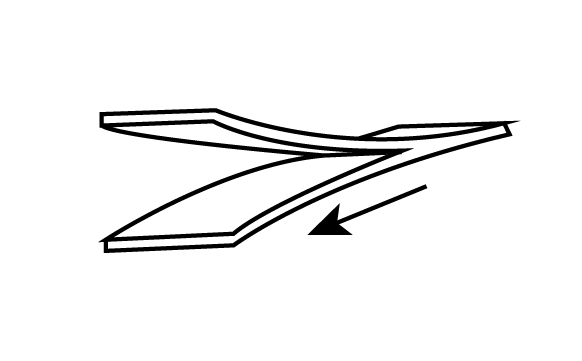
In crocodile crack, the metal sheet splits into two parts due to weakness at the center. The diagrammatical representation of crocodile crack is shown as:
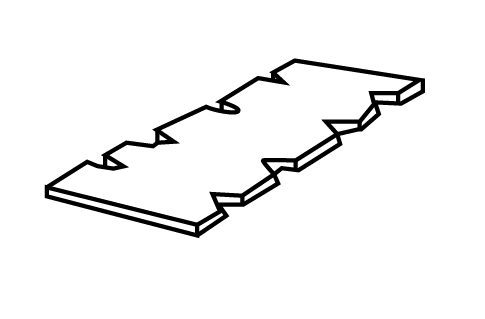
Alligatoring
Alligatoring is a defect caused by non-uniform deformation during the metal rolling or the presence of defects in the original raw material or alloy. The diagrammatical representation of the alligatoring is shown as:
Extrusion defect
In the extrusion process, if the temperature, friction, and speed are high, it will increase surface temperature, which enables surface cracking and tearing. The extrusion defects occur mainly in aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys. Following are the various types of extrusion defects:
- Pipe defect
- Surface cracking
- Internal cracking
Pipe defect
In pipe defects, an unusual metal flow pattern tends to draw surface impurities towards the center of the metal billet. It is also called tailpipe and fishtailing. This defect is overcome by controlling friction and minimizing temperature gradients.
Surface cracking
Surface cracks and tears occur mainly due to a significant rise in surface temperature. The surface temperature rises due to high speed and high friction. The surface cracking is possible at low temperature because of periodic sticking of extruded product with extrusion die.
Internal cracking
Internal cracking is also termed center cracking and arrowhead fracture. The internal cracks occur due to a state of hydrostatic tensile stresses at the centerline of the die's deformation zone. The center or internal cracking mainly occurs due to increasing die angle, increasing amount of impurity, using false alloy and increasing friction.
Drawing defects
Following are the defects that occur in metal during the drawing process:
- Wrinkle
- Fracture
- Earing
- Miss Strike
- Orange Peel
Wrinkle
Wrinkles are developed over the flange surface due to insufficient blank holder. They also extend to the surface of the cup. The diagrammatical representation of wrinkle is shown as:
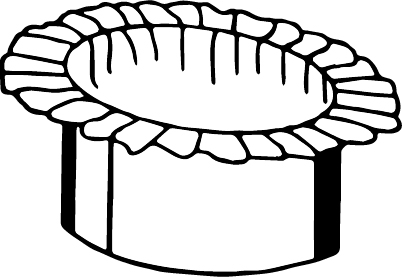
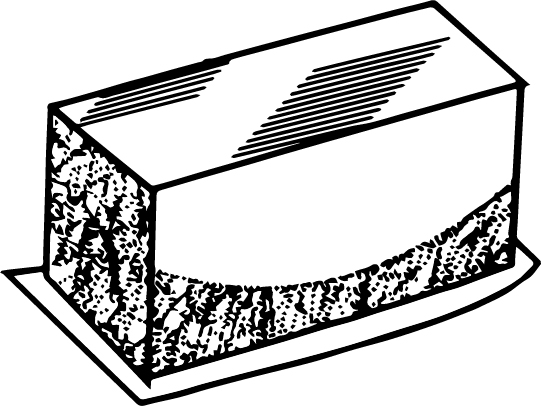
Fracture
Fracture commonly occurs in a flange, bottom, and corners of drawing because of high blank hold pressure and friction. The diagrammatical representation of drawing fracture is shown as:
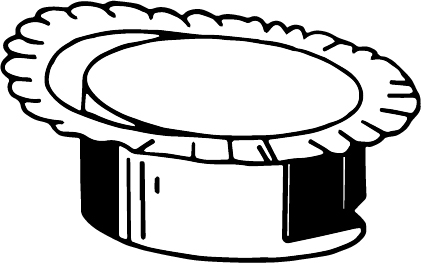
Earing
In the drawing process, earing or lobes occurs mainly at the initial position due to improper distribution of load on raw material. The diagrammatical representation of earing is shown as:
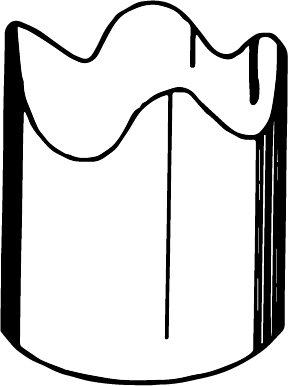
Miss strike
In miss strike, unsymmetrical flanges are produced due to misplacement of the stock. The diagrammatical representation of miss strike is shown as:
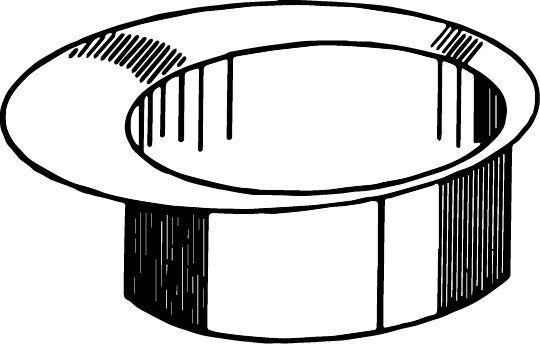
Orange peel
Orange peel is a surface roughening defect generated in forming products from the metal stock of coarse grain size. The diagrammatical representation of orange peel is shown as:
Common Mistakes
Following are the common mistakes performed by students:
- Sometimes, students get confused about the factors on which the microstructure of crystal depends.
- Sometimes, students get confused about various metal defects based on their manufacturing process.
- Sometimes, students get confused between slag inclusion and impurity inclusion.
- Sometimes, students forget the reason for extrusion defects.
Context and Applications
The topic of identifying microstructure and defects in metalworking is significant in various courses and professional exams of undergraduate, graduate, postgraduate, doctorate levels. For example:
- Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical Engineering
- Bachelor of Technology in Production Engineering
- Diploma in Mechanical Engineering
- Bachelor of Science in Microtechnology
- Master of Technology in Production Engineering
Following are the various applications of identifying microstructure of material:
- To identify the characteristics of the material.
- To understand the association of material properties with their crystal structure.
- To identify properties of materials.
- To design alloys with new or desired properties.
- To check the material is correctly processed or not during various processes.
Related Concepts
- Crystal defect
- Corrosion
- Behavior of metals with chemical
- Manufacturing defects
- Alloys
Practice Problems
Q1. Microstructure depends on which of the following factor?
- Crystal defect
- Phase arrangement
- Crystal structure
- All of the above
Correct option: (d)
Explanation: The microstructure is represented as an arrangement of grains in the element's physical structure that is identified by using an instrument named microscope. Also, the microstructure does get affected by the variation in crystal defect, phase arrangement, crystal structure, and many others.
Q2. Line defect is which of the following metallic defect?
- Crystal structure
- Metal forming
- Fabrication
- Casting
Correct option- (a)
Explanation: Line defects take place in any metal due to its crystal structure. The effect of line defect is that it weakens the solid material.
Q3. Frenkel defect is ______ defect?
- Dimensionless
- One dimensional
- Two dimensional
- Three dimensional
Correct option: (a)
Explanation: A Frenkel defect is one of the types of defect that occurs due to occupying a vacant space by a particular atom in a crystal. Also, Frenkel defects are also termed as dimensionless defects.
Q4. Which of the following is not a rolling defect?
- Wavy edges
- Crocodile crack
- Spread
- Wrinkle
Correct option: (d)
Explanation: Some of the common rolling defects are wavy edges, edge cracks, alligator cracks, spread, and others. On the other hand, wrinkling occurs in deep drawing processes when overheating the job.
Q5. Which of the following defect is called fishtailing?
- Wavy edges
- Wrinkle
- Pipe defect
- Crocodile crack
Correct option: (c)
Explanation: Fishtailing is a type of pipe defect which happens due to the existence of contaminants while performing the extrusion process.
Want more help with your mechanical engineering homework?
*Response times may vary by subject and question complexity. Median response time is 34 minutes for paid subscribers and may be longer for promotional offers.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.
Materials Science and Engineering
Solidification and Crystalline Imperfections
Identifying Microstructure and Defects in Metals
Identifying Microstructure and Defects in Metals Homework Questions from Fellow Students
Browse our recently answered Identifying Microstructure and Defects in Metals homework questions.
Search. Solve. Succeed!
Study smarter access to millions of step-by step textbook solutions, our Q&A library, and AI powered Math Solver. Plus, you get 30 questions to ask an expert each month.