
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.2, Problem 1hT
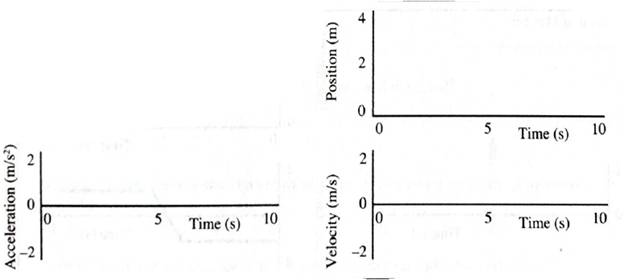
Description of Motion:
Move toward the detector with decreasing speed, then just as you have come to rest, move away, from the detector with increasing speed.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:48
Students have asked these similar questions
Imagine you are boarding on taxi moving at a constant velocity, what will happen to you when a driver suddenly applies the break.
How does changing the initial height of where a ball is thrown and the angle of which a ball is thrown may impact the projectiles motion.Explain using physics concepts
A ball moving at an initial velocity of 5 m/s rolls off a table that measures 2 m height. With those measurements, determine the range of the ball. Round to the nearest hundredth. Use IGUESS method.
Chapter 1 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - Each person in your group should obtain a ruler...Ch. 1.1 - A. In the space below, sketch a possible ticker...Ch. 1.1 - B. Together with your classmates, take your ticker...Ch. 1.1 - C. Based on your observations of your tape segment...
Ch. 1.1 - D. Review your earlier interpretation of the speed...Ch. 1.1 - E. Suppose you selected two widely separated dots...Ch. 1.2 - The computer program assumes a particular...Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - How are the motions in parts C and D similar? How...Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion: Move toward the detector...Ch. 1.2 - How do the acceleration graphs for F, G, and H...Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion: Initially move away from...Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - Description of Motion:Ch. 1.2 - The term decelerate is often used to indicate that...Ch. 1.3 - Draw vectors on your diagram that represent the...Ch. 1.3 - B. In the space at right, compare the velocities...Ch. 1.3 - Consider the change in velocity vector between two...Ch. 1.3 - Use the definition of acceleration to draw a...Ch. 1.3 - Does the acceleration change as the ball rolls up...Ch. 1.3 - Generalize your results thus far to answer the...Ch. 1.3 - Choose two successive points. In the space at...Ch. 1.3 - In the space at right, draw a vector to represent...Ch. 1.3 - Choose a point before the turnaround and another...Ch. 1.3 - Suppose that you had chosen the turnaround as one...Ch. 1.3 - In the space at right, draw a vector that...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 1aTCh. 1.4 - If you were to choose a different origin for the...Ch. 1.4 - On a separate part of your paper, copy the...Ch. 1.4 - Suppose you were to choose a new point on the...Ch. 1.4 - On a separate part of your paper, copy the...Ch. 1.4 - Suppose the object started from rest at point E...Ch. 1.4 - At several points on each of the diagrams below,...Ch. 1.5 - The second diagram at right shows the positions of...Ch. 1.5 - The picture of the spaceships and shuttle from the...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1cTCh. 1.5 - Spaceship C moves so as to remain a fixed distance...Ch. 1.5 - Consider the following statement: "The...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1fTCh. 1.5 - Describe the motion of the car and the truck...Ch. 1.5 - Complete the diagram at right by drawing the car...Ch. 1.5 - Use your completed diagram to sketch average...Ch. 1.5 - During a small time interval t from just before to...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
22. Why are residents of northern Canada less shielded from cosmic rays than are residents of Mexico?
College Physics
Why don't we operate ocean liners by extracting heat from the ocean or operate airplanes by extracting heat fro...
University Physics Volume 2
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. What is the name of the rigid outer la...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
22. A bird flies 3.0 km due west and then 2.0 km due north. What is the magnitude of the bird's displacement?
2...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
24. Small frogs that are good jumpers are capable of remarkable accelerations. One species reaches a takeoff sp...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
4.52 CALC The position of a training helicopter (weight 2.75 × 105N) in a test is given by = (0.020 m/s3)t3 + ...
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
An object is dropped from a height of 75.0 m above ground level. (a) Determine the distance traveled during the first second. (b) Determine the final velocity at which the object hits the ground. (c) Determine the distance traveled during the last second of motion before hitting the ground.
arrow_forward
Which is true of an object with uniform velocity? (2.2) (a) It has constant speed. (b) It has constant direction. (c) It travels equal distances in equal times. (d) All of the preceding.
arrow_forward
An object is in motion when it undergoes a continuous change of ___. (2.1)
arrow_forward
Compare the distance traveled of an object that undergoes a change in velocity that Is twice its initial velocity with an object that changes its velocity by four times its initial velocity over the same time period. The accelerations of both objects are constant.
arrow_forward
I need help with a University Physics 1 (Finding velocity and Displacement from Acceleration) - The problem is described in the image below:
arrow_forward
Constant velocity motion requires that the objects..
A) be moving at constant speed
B) be moving in an unchanging direction
C) either A or B
D) both A & B
arrow_forward
A total distance of travel of 1,000 km breaks every 100 km of a pattern of East-South-East-South continuously up to the end. The time of travel was recorded 5 hours.
a. Find the average velocity of the travel.
b. If a helicopter flies from the same origin, what will be its average velocity in an hour travel?
arrow_forward
An object is dropped from a height of 75.0 m aboveground level. (a) Determine the distance traveled during thefirst second. (b) Determine the final velocity at which theobject hits the ground. (c) Determine the distance traveledduring the last second of motion before hitting the ground.
arrow_forward
Tom, the cat, is chasing Jerry, the mouse. Jerry runs past Tom at a constant velocity of 19 m/s. The instant Jerry passes Tom, Tom starts from rest and accelerates at 3.59 m/s2. What is the velocity of Tom when he catches up to Jerry?
Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
arrow_forward
A ball player catches a ball 3.71 seconds after throwing it vertically upward. With what speed did he throw it? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
arrow_forward
Amina throws the ball straight upward and after 1 second it reaches its maximum height then it does free fall motion which takes 2 seconds. Calculate the maximum height and the velocity of the ball when it reaches the same level on its way down (take g = 10 m/s2)
arrow_forward
Draw the four graphs of the x and y components of position, velocity versus time of projectile.
(Correction: The last graph should be Y-velocity versus time graph. )
arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College
Speed Distance Time | Forces & Motion | Physics | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EGqpLug-sDk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY