
Concept explainers
Suppose that a single change were made to the apparatus (keeping the distance between the mask and the screen fixed), resulting in the new pattern shown.
1. Are the angles to the interference maxima in the new pattern greater than, less than, or equal to those in the original pattern? Explain how you can tell from the photographs.
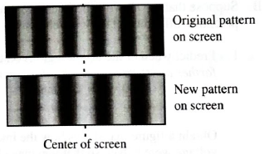
2. If the
3. If the slit separation (d) was the only quantity changed, determine (i) whether d was increased or decreased, and (ii) whether it was changed by a factor that was greater than, less than, or equal to 2. Explain how you can use your results from parts A and B to justify your answer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 14 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Physics (5th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)

